Importance of Betaine trimethylglycine (TMG)
The importance of betaine
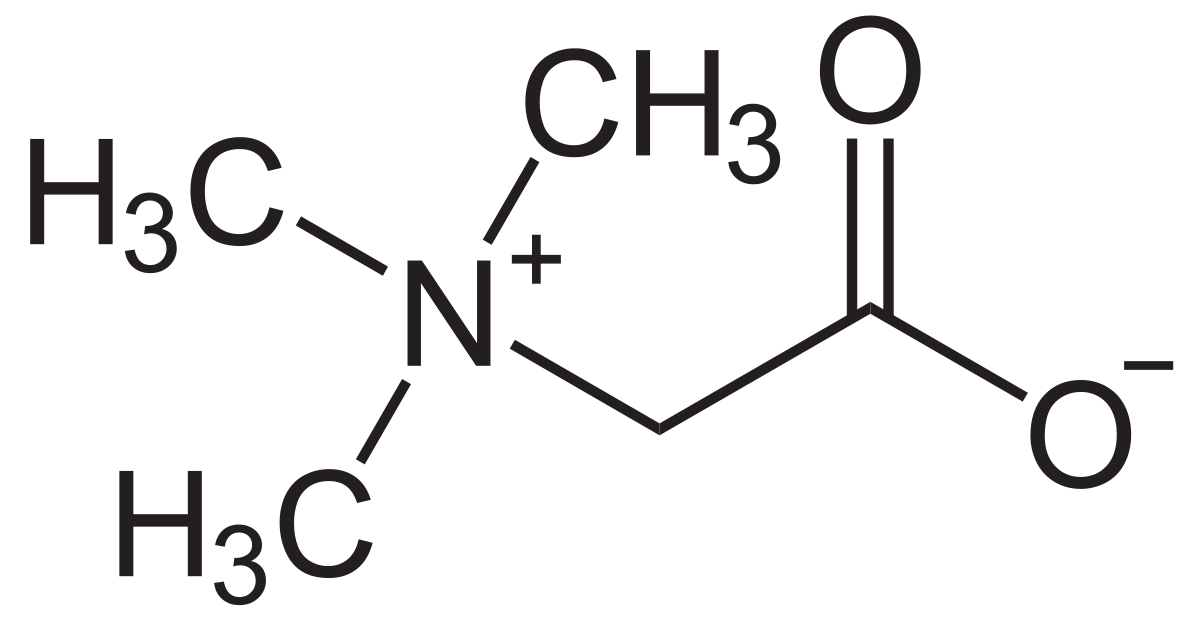
Betaine, also known as trimethylglycine (TMG), has become increasingly popular in dietary supplements, but in reality, it is not a newly discovered nutrient.
What is betaine?
The professional name of betaine is "trimethylglycine", which is a derivative of choline. In other words, choline is a precursor to betaine, and choline must be present in the body to be synthesized into betaine.
What are the effects of betaine supplements?
In the field of medicine, many excellent pharmacological effects of betaine have been discovered, which can be used to combat hyperhomocysteine syndrome, protect the liver and kidneys, maintain heart and vascular health, maintain the digestive system, inhibit tumors and cancer, reduce blood pressure and sedation, relieve fever and pain, and resist hypoxia to protect cells from high osmotic pressure. According to literature reports, betaine has various pharmacological effects such as promoting fat metabolism, anti fatty liver, protecting the kidneys, lowering blood pressure, relieving stress, enhancing appetite, and stabilizing vitamins. Betaine was initially used as a protective agent for the liver, stomach, and heart, and has a mild antihypertensive effect.
Symptoms of a lack of betaine in the body
Betaine deficiency is not common in Western countries, mainly due to sufficient dietary intake. Because betaine is high in wheat products, which are the staple food for most people.
What problems do you encounter when you don't eat foods rich in betaine? Excessive intake of foods rich in betaine may lead to high levels of homocysteine in the blood. Although there may be many reasons for high levels of homocysteine in the blood, including environmental factors, diet, and genetics.
Severe elevation of homocysteine levels can lead to developmental problems, osteoporosis, visual abnormalities, thrombosis, narrowing of blood vessels, and sclerosis.

 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 CA
CA
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 KA
KA
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 PA
PA
 TA
TA
 TE
TE
 LB
LB
